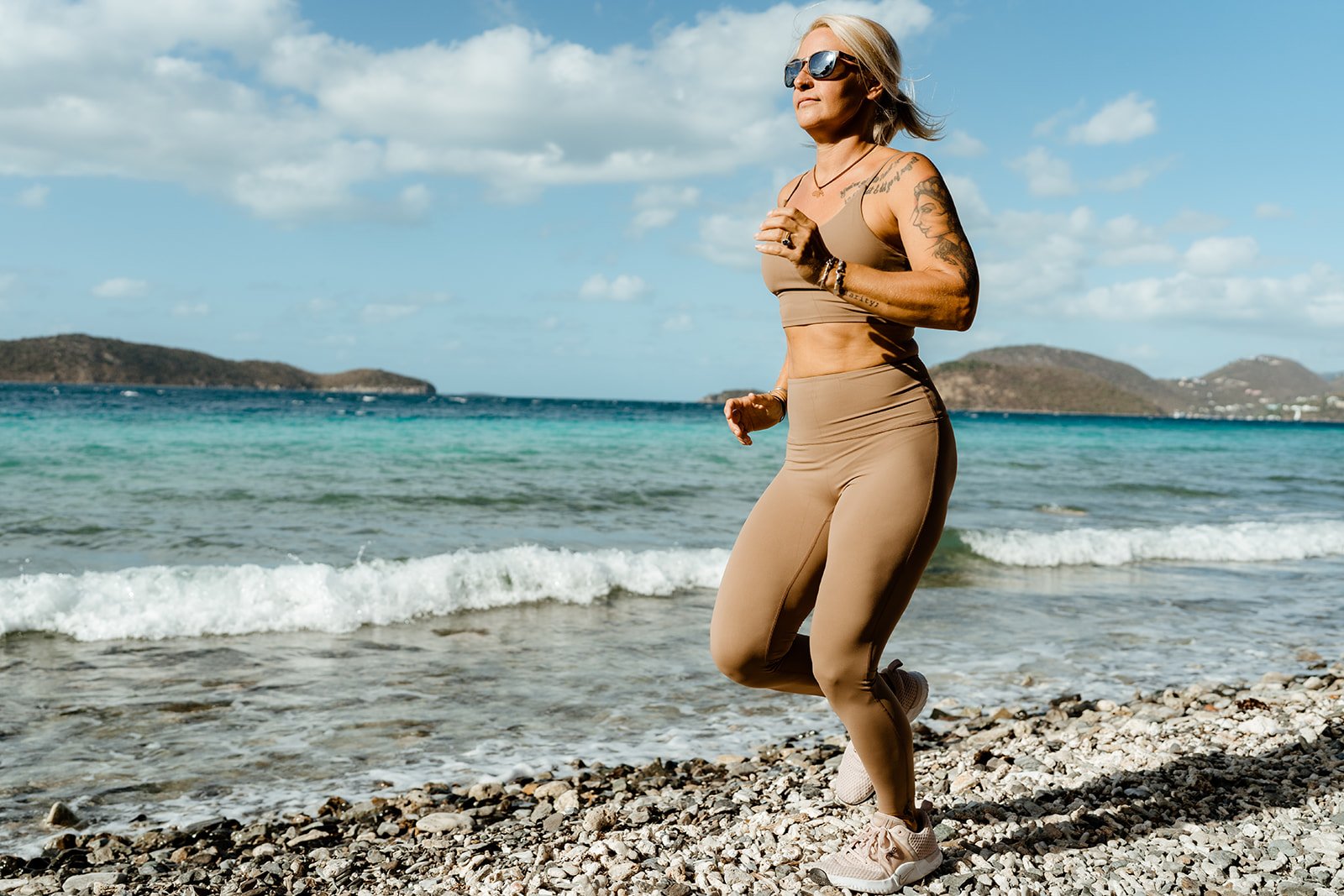
8 ways diet can affect your energy
diet plays a crucial role in influencing energy levels. the food we consume provides the body with the necessary nutrients—ahem, carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, and minerals! these nutrients serve various functions in the body, impacting energy production and overall well-being. here's how diet affects energy:
carbohydrates for energy:
carbohydrates are the body's primary source of energy. when you consume carbohydrates, they are broken down into glucose (sugar), which is then used by cells for energy.
complex carbohydrates, found in whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, provide a more sustained release of energy compared to simple carbohydrates, such as refined sugars.
proteins for sustained energy:
proteins are essential for the repair and maintenance of body tissues. while they are not the primary source of energy, they play a role in providing a more sustained release of energy and can be used as an energy source when carbohydrates are insufficient.
fats for long-term energy storage:
fats are a concentrated source of energy and are stored in the body for long-term energy use. consuming healthy fats, such as those found in avocados, nuts, and olive oil, can contribute to sustained energy levels.
micronutrients for energy metabolism:
vitamins and minerals, such as B-vitamins and iron, are crucial for energy metabolism. they facilitate the conversion of food into energy and play a role in maintaining overall health.
hydration for energy:
dehydration can lead to fatigue and decreased energy levels. staying adequately hydrated is essential for proper bodily functions, including energy production.
meal timing and frequency:
eating regular, balanced meals helps maintain stable blood sugar levels, preventing energy crashes. skipping meals or relying on irregular eating patterns can lead to fluctuations in energy levels.
nutrient balance:
a well-balanced diet ensures that the body receives all the necessary nutrients in the right proportions. nutrient imbalances, such as excessive consumption of refined sugars or inadequate intake of essential nutrients, can negatively impact energy levels.
individual variations:
individual responses to different foods can vary. some people may thrive on a higher-carbohydrate diet, while others may feel more sustained energy with a higher proportion of fats or proteins.
so! the next time you reach for more caffeine, take a look at your diet first.
it's important to note that individual factors, such as age, activity level, and health conditions, can also influence how diet affects energy levels. consulting with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian can help create a personalized nutrition plan that meets individual needs and supports optimal energy levels.